Topological sort to order character in an alien dictionary
Problem Statement:
Given a sorted dictionary of an alien language, you have to find the order of characters in that language. Generally, dictionary does not contain duplicate values, but for the sake of this problem, assume that dictionary might have duplicate values. (Sometimes interviewer tricks the question, to see, how you will handle it.)
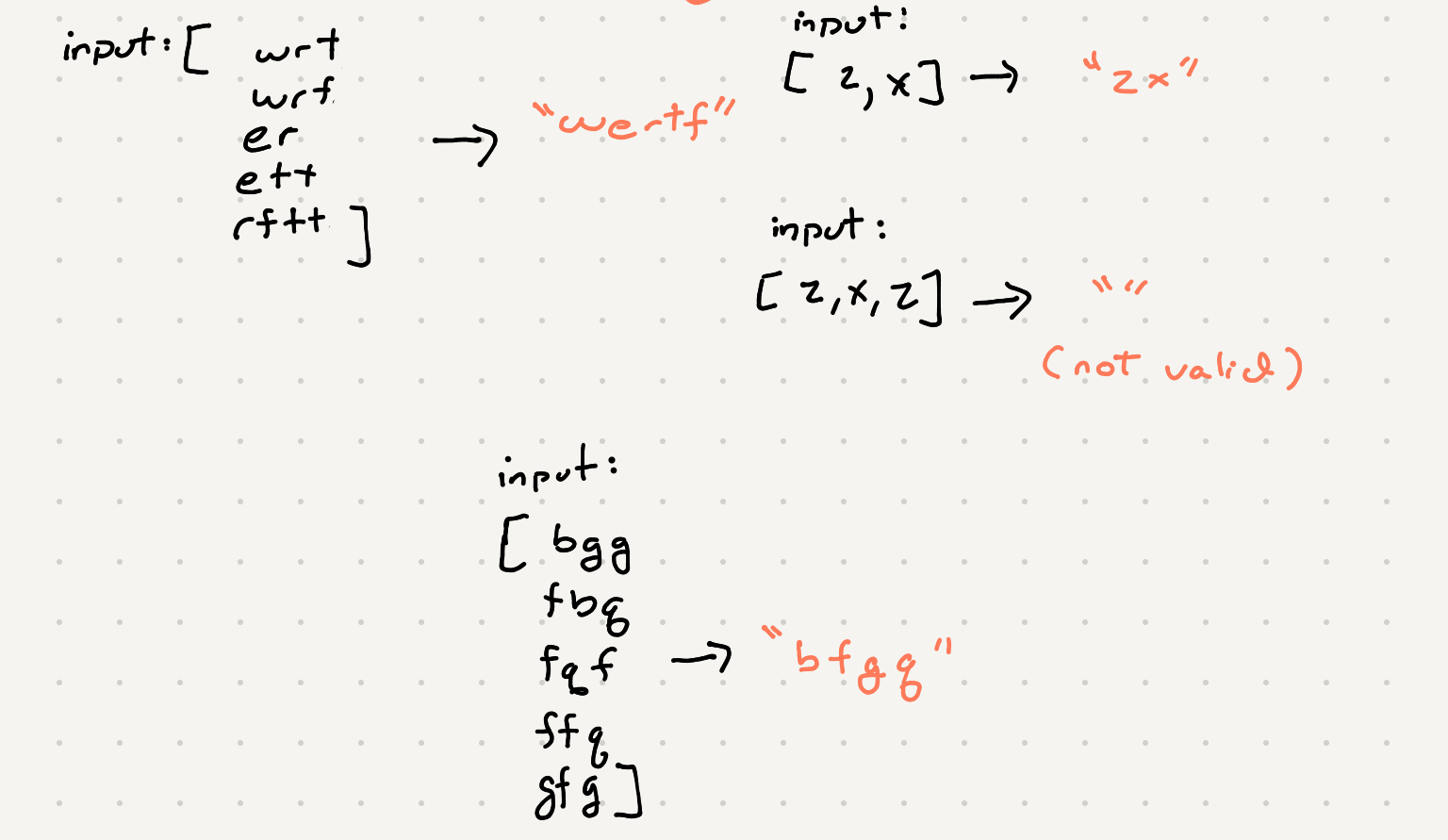
So first let’s try to understand the inputs here so we can make some assumptions.
We can see if we compare the first letter of these words we know that we can make an assumption that word[0] goes before word[1] ie b -> f.
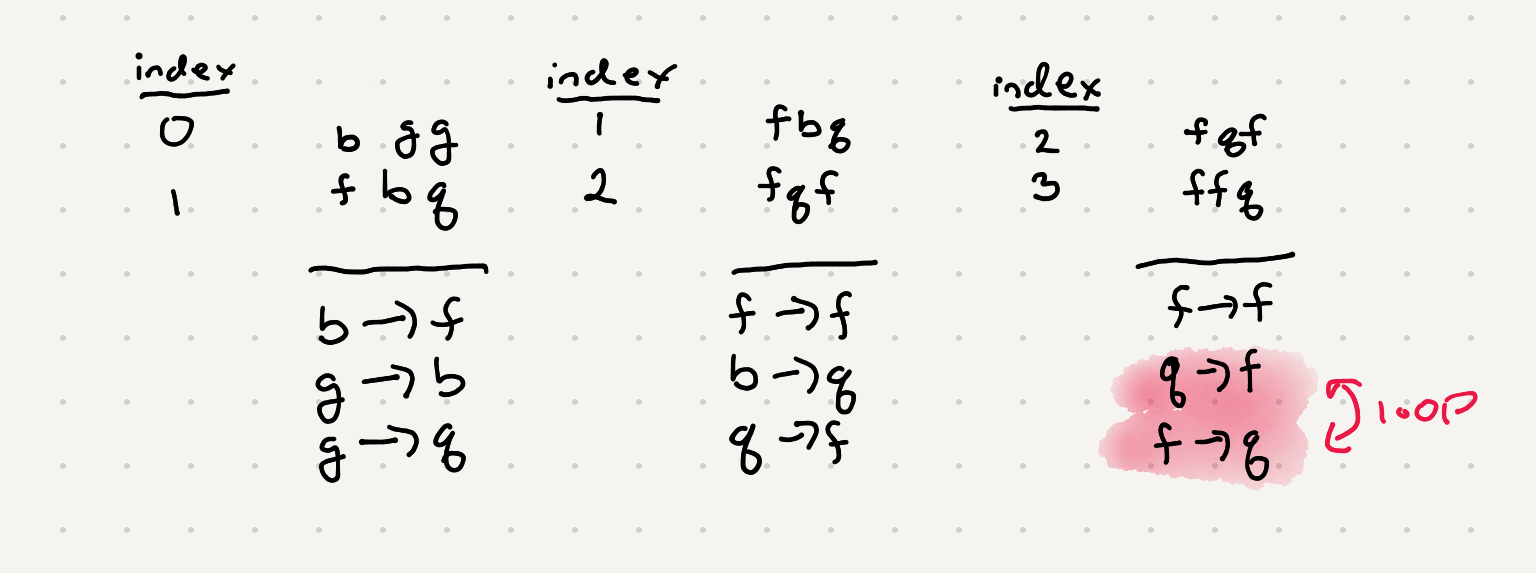
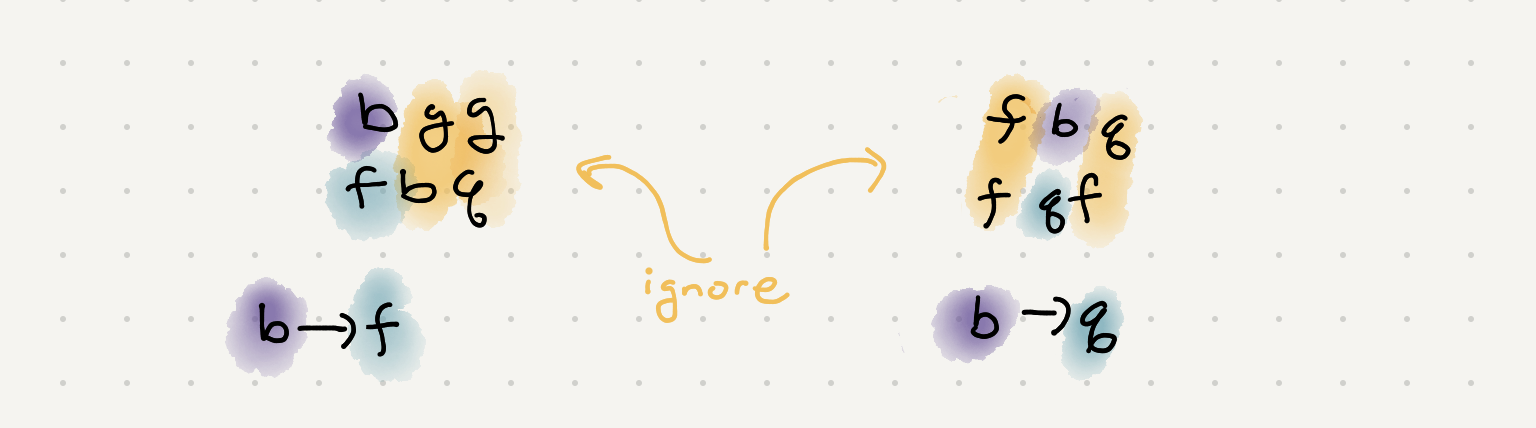
If we were to iterate thought all the words and all the chars we can build up a list of associations. We have to be careful however because we can’t really compare letters other than the first of the word. For example if we compare fqf and ffq we end up with a loop that doesn’t make any sense ie f > q and q > f.
We can definitely compare the first letters of a pair of words but the remaining letters don’t give us an accurate portrayal of the dictionary. But what about the case if some of the letters the same? Well that means the next letter is the tiebreaker. We can keep iterating though both words until we find that tiebreaker and those char can in turn make a valid connection. Once we have that connection we should stop processing char since we can’t make a valid assumption in the ordering of the letters.
Let’s recap our assumptions so far for making connections
- compare the first letter of each word.
word1[0] < word2[0] - if there is a tie find the tiebreaker.
word1[index_of_first_diff_char] < word1[index_of_first_diff_char]
Using our assumptions lets build this connection mapping for our input
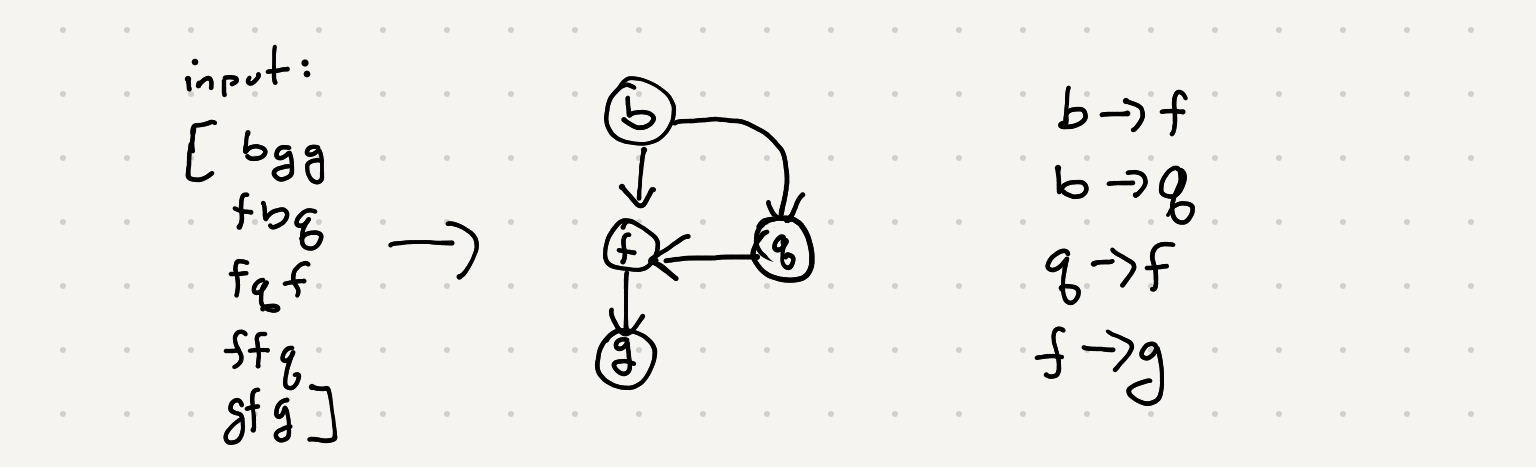
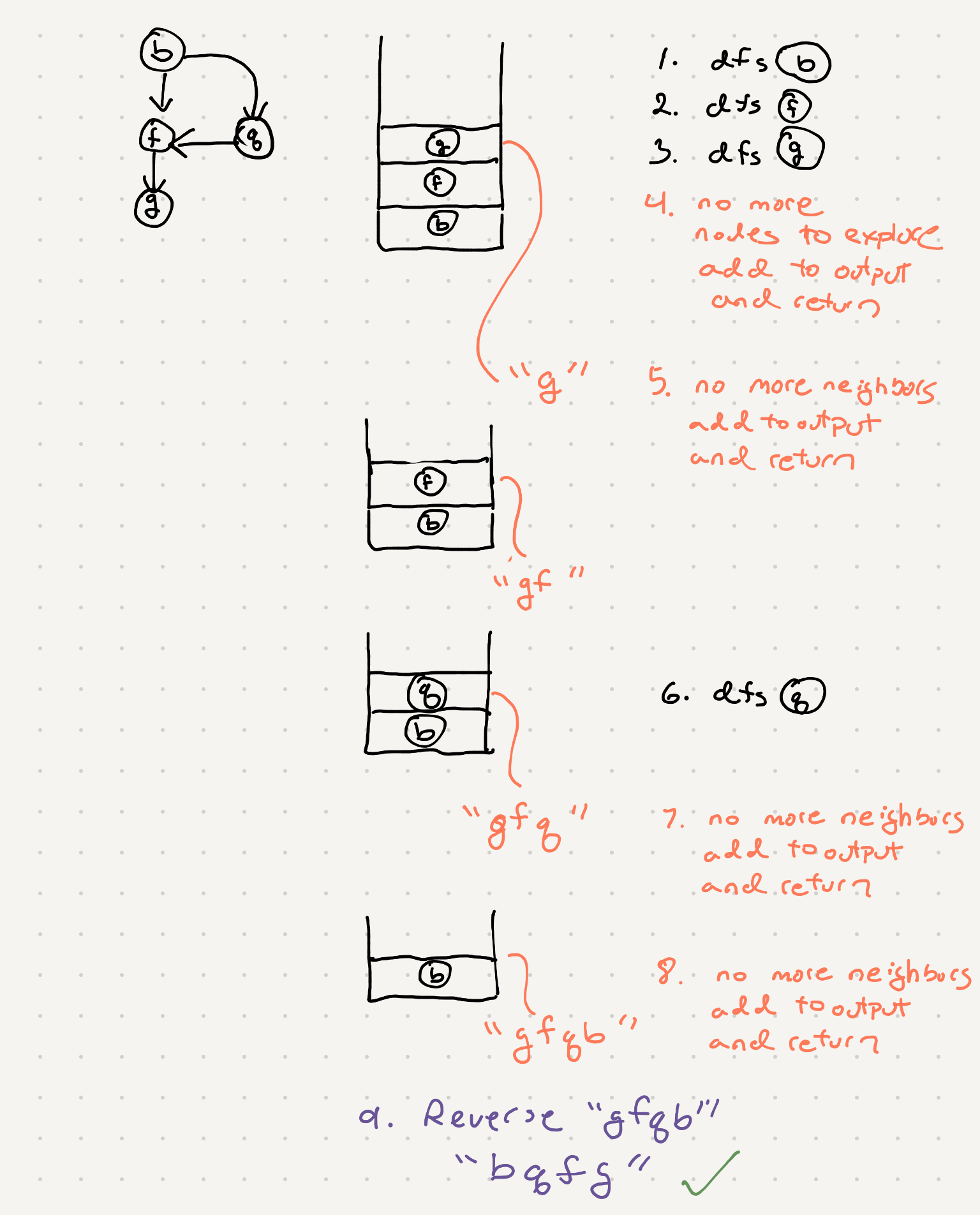
So we have a list of associations now. At this point we can see these associations can be represented by a graph. In a previous post we’ve looked at generating course schedules given dependencies using dfs and topological sort. Topological sort only works for a graph with no cycles. Recall earlier we made an effort in our connection generation to avoid loops. If we simply traverse our graph using dfs we’ll be able to generate a proper ordering of the letters in this alien dictionary
We have another scenario we need to think about. What happens in the case where we have letters that don’t have an association? For example
['z', 'z'] -> this should just return 'z'
Recall in dfs graph algorithms we usually have an for loop before our dfs call to make sure we traverse all nodes that aren’t connected. In our case we need to populate our graph with all the chars that aren’t connected. We can iterate through every char in every word and generate a set. We can then use this set and associations to represent our graph
def build_graph(words):
for word in words:
for char in word:
char_list.add(char)
words_len = len(words)
for i in range(words_len - 1):
in_word = words[i]
out_word = words[i + 1]
min_char_to_compare = min(len(in_word), len(out_word))
for x in range(min_char_to_compare):
# insert a relationship
if in_word[x] != out_word[x]:
adj_list[in_word[x]].add(out_word[x])
# important to stop here because we can't
# guarentee that the next comparison is true
break
So now that we have the graph we can use the same dfs topological sort algorithm from the course scheduling problem to wire everything up.
from collections import defaultdict
def build_graph(words):
# we need to handle all chars seen from words.
# ex if we have mismatched word sizes we still
# take care of leftover letters
for word in words:
for char in word:
char_list.add(char)
words_len = len(words)
for i in range(words_len - 1):
in_word = words[i]
out_word = words[i + 1]
min_char_to_compare = min(len(in_word), len(out_word))
for x in range(min_char_to_compare):
# insert a relationship
if in_word[x] != out_word[x]:
adj_list[in_word[x]].add(out_word[x])
# important to stop here because we can't
# guarentee that the next comparison is true
# ex.
break
def dfs_topo_sort(node):
if node in seen:
if seen[node] == "VISITING":
has_cycle[0] = True
return
seen[node] = "VISITING"
for neighbor in adj_list[node]:
dfs_topo_sort(neighbor)
# we are visiting in reverse order so append to the front
letter_order.append(node)
seen[node] = "VISITED"
# build adj list
adj_list = defaultdict(set)
char_list = set()
build_graph(words)
# dfs topological sort on this graph
seen = {}
letter_order = []
has_cycle = [False]
for node in char_list:
if node not in seen:
dfs_topo_sort(node)
if not letter_order or has_cycle[0]:
return ""
# DFS returns results in reversed order
return "".join(reversed(letter_order))
The time complexity of traversing the graph is O(V+E)