MergeSort - step by step
Mergesort is a divide and conquer algorithm. It breaks down an array into halves and solves the problem on the left, solves the problem on the right and then merges those two results together
def mergesort(array):
array_length = len(array)
if array_length <= 1:
return array
# sort the left side
left_side = mergesort(array[:n/2])
# sort the right side
right_side = mergesort(array[n/2:1])
# merge the results
return merge(left_side, right_side)
The divide part can be visualized like this
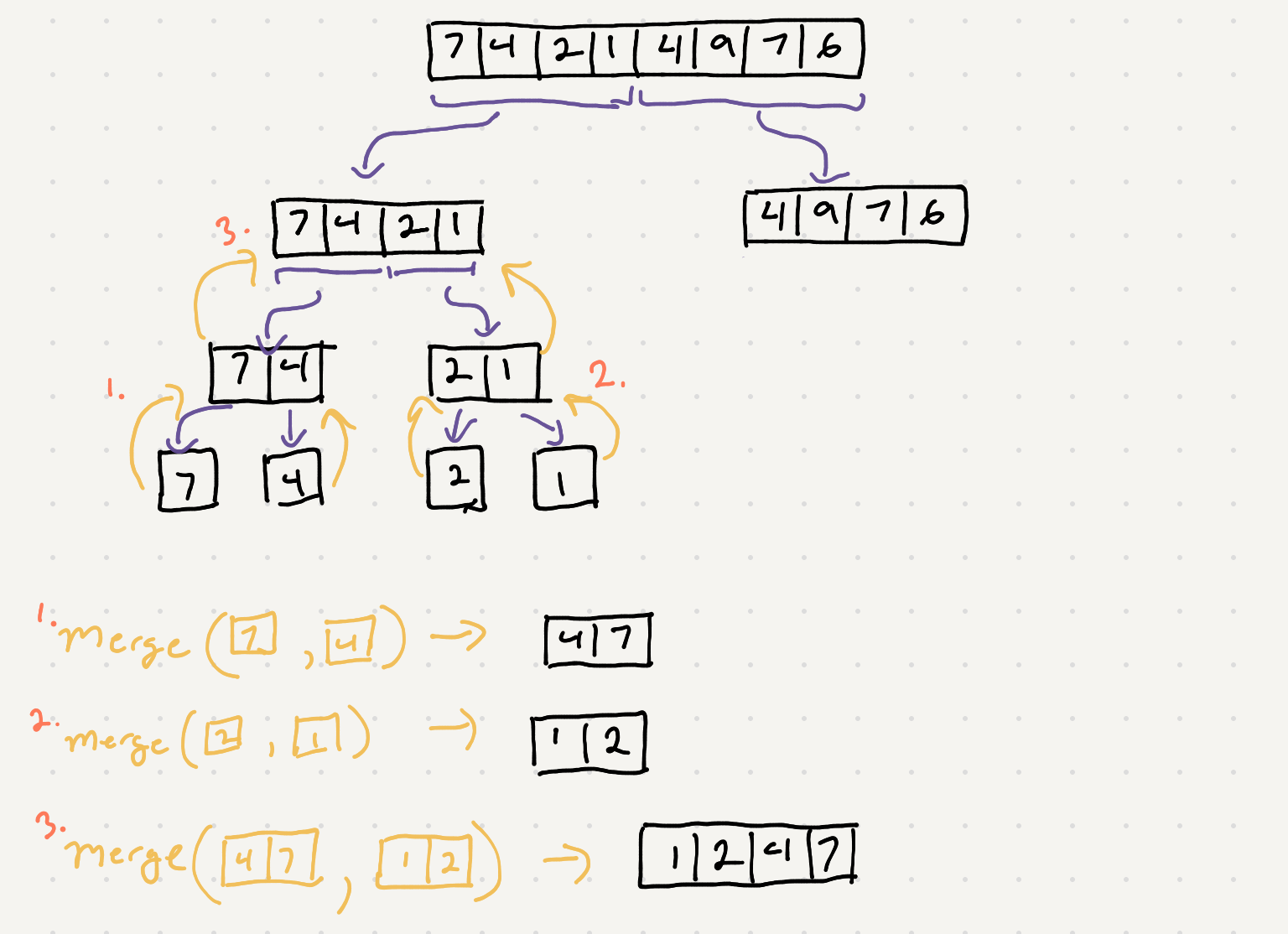
Ok so how do actually do the merge of the two halves? Recall because of the divide and conquer approach the merge function will be called with two sorted arrays. Another way of saying this is that both the inputs of merge are completely sorted.
One thing we can do is maintain 2 pointers that point to each half of input. We also maintain a third pointer to populate our auxiliary space needed for the merge.
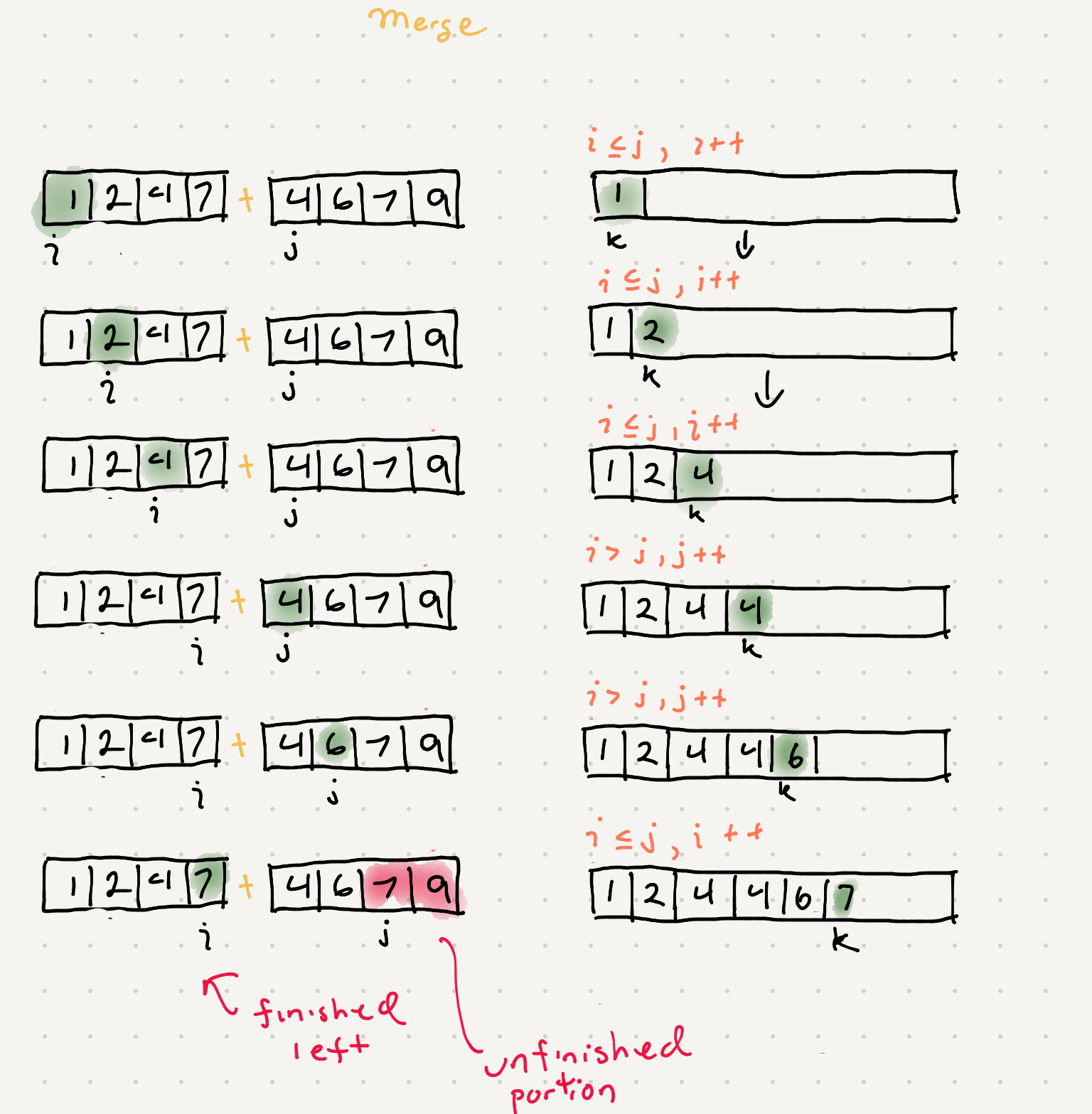
So we can just iterate through the left and right sides and do some comparisons
i = j = k = 0 # i left side pointer, j right side pointer
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
# left side has smaller value
if left[i] < right[j]:
aux[k] = Left[i]
i+=1
else:
aux[k] = right[j]
j+=1
k+=1
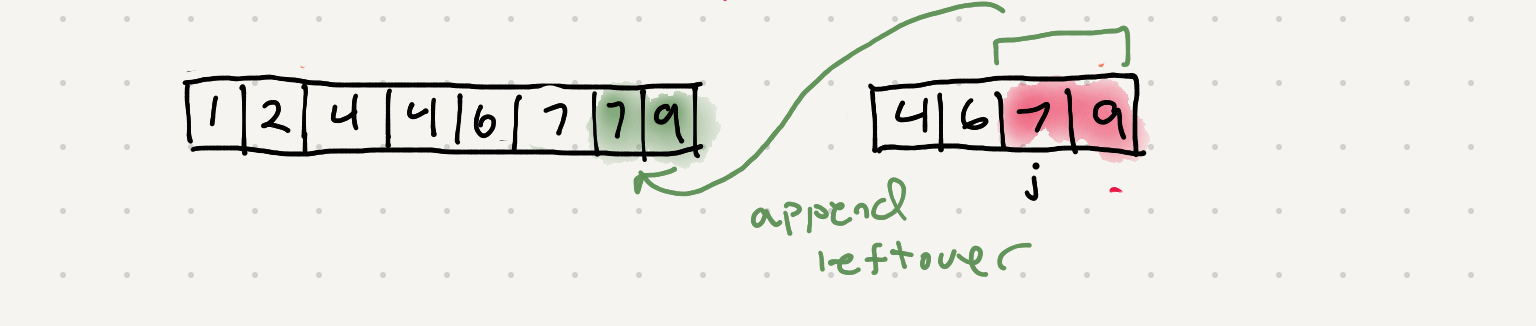
So this will iterate completely through one array but what about when we have leftover portion of another array? We’ll need a way to merge the remainder of the unfinished array into the aux space.
# Checking if any unfinished on the left
while i < len(left):
aux[k] = left[i]
i+=1
k+=1
# Checking if any unfinished on the right
while j < len(right):
aux[k] = right[j]
j+=1
k+=1
Putting it all together we have
def mergesort(array):
array_length = len(array)
if array_length <= 1:
return array
# sort the left side
left_side = mergesort(array[:n/2])
# sort the right side
right_side = mergesort(array[n/2:1])
# merge the results
i = j = k = 0 # i left side pointer, j right side pointerjj
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
# left side has smaller value
if left[i] < right[j]:
array[k] = Left[i]
i+=1
else:
array[k] = right[j]
j+=1
k+=1
# Checking if any unfinished on the left
while i < len(left):
array[k] = left[i]
i+=1
k+=1
# Checking if any unfinished on the right
while j < len(right):
array[k] = right[j]
j+=1
k+=1
return array
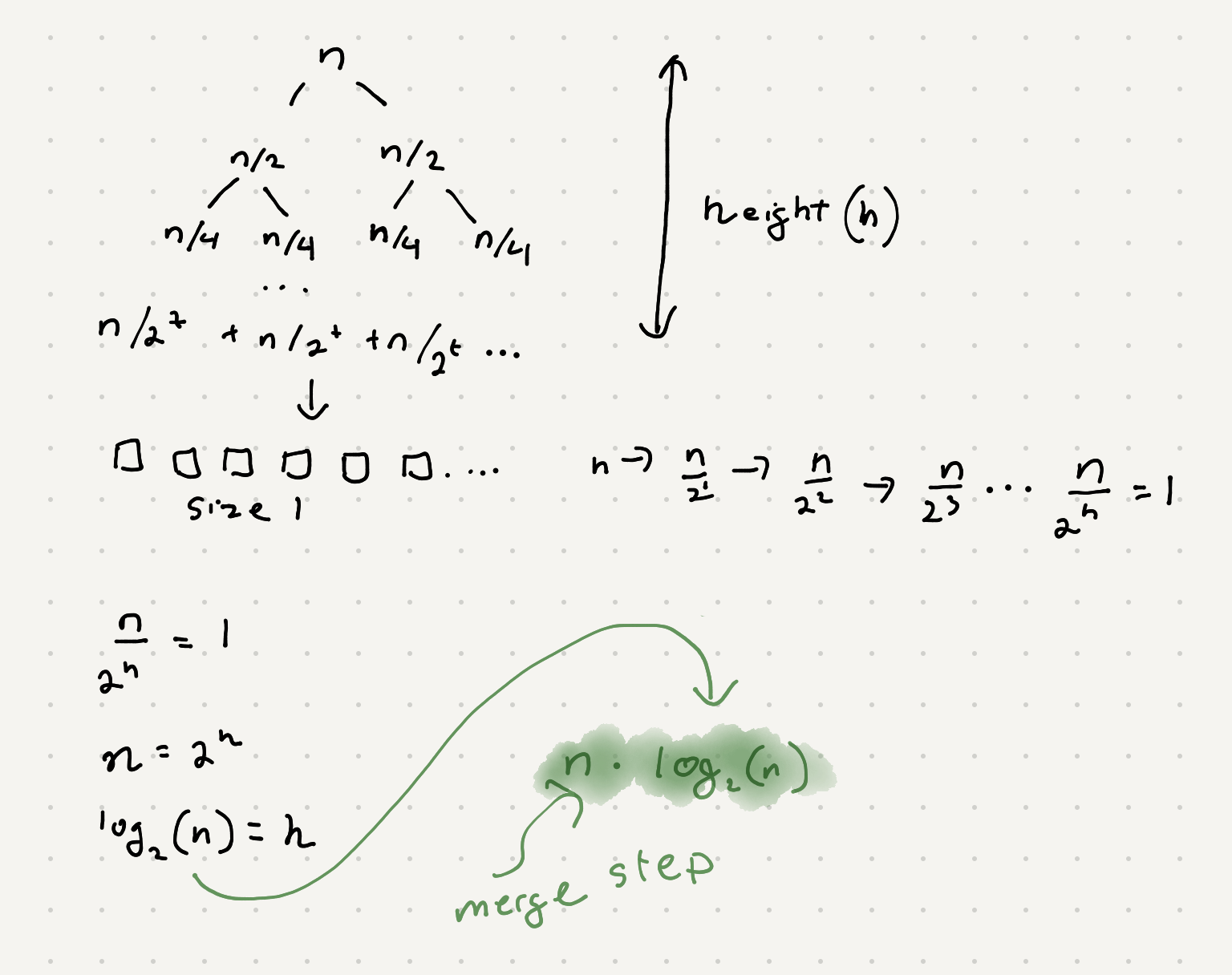
The time complexity of mergesort will be nlog(n).