Quicksort - step by step
Tags:
sorting
There are plenty of resources to learn quicksort but I didn’t feel like I fully understood the details until I drew out the recursion tree and actually stepped through the partition function.
def quicksort(array):
def partition(begin, end):
pivot = begin
for i in range(begin + 1, end + 1):
if array[i] < array[begin]:
pivot += 1
array[i], array[pivot] = array[pivot], array[i]
array[pivot], array[begin] = array[begin], array[pivot]
return pivot
def _qs(begin, end):
if begin >= end:
return
p = partition(begin, end)
_qs(begin, pivot-1)
_qs(pivot+1, end)
return _qs(0, len(array) - 1)
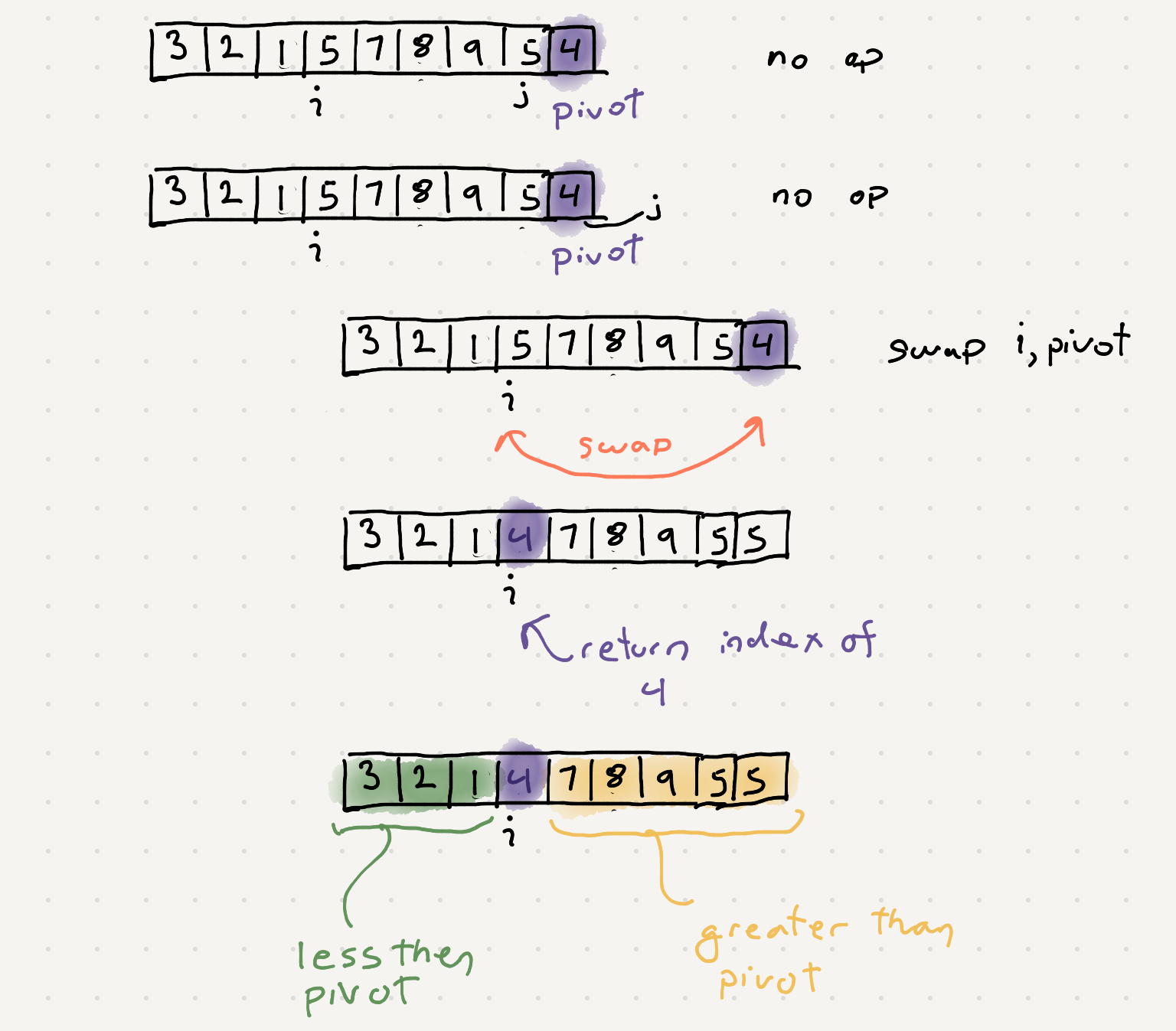
So let’s take a look at the partition function and see how it modifies the array after picking the rightmost element as the pivot point

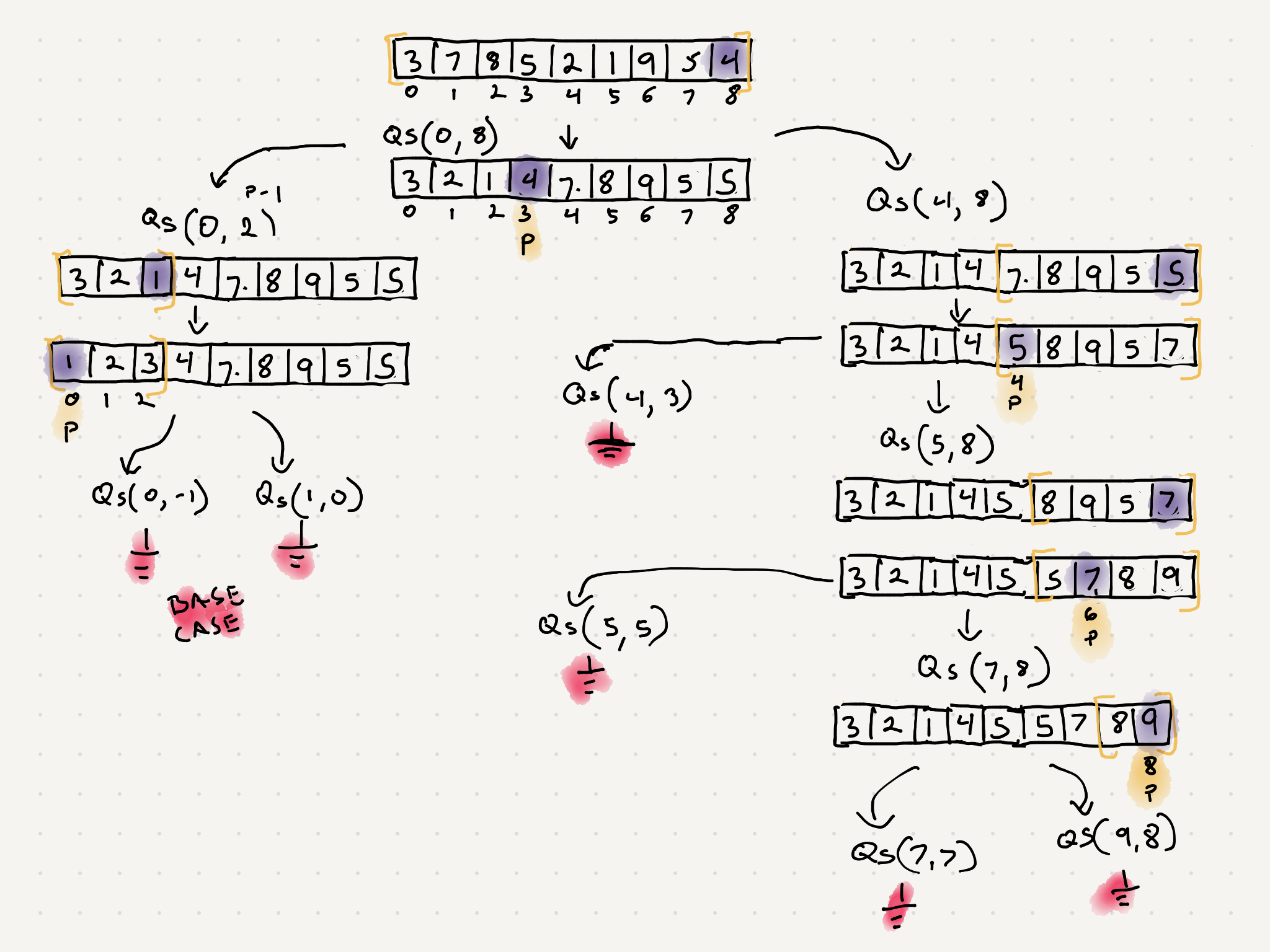
Let’s look at the recursion tree and see how our divide and conquer algo breaks up the array into subarrays/problems