Given A Graph, Build A New One With Reversed Edges
Problem Statement:
Given a strongly connected directed graph G, containing n nodes and m edges, you have to build a new graph containing n nodes, where edges are reversed than the original graph G. This is also called Transposing the graph.
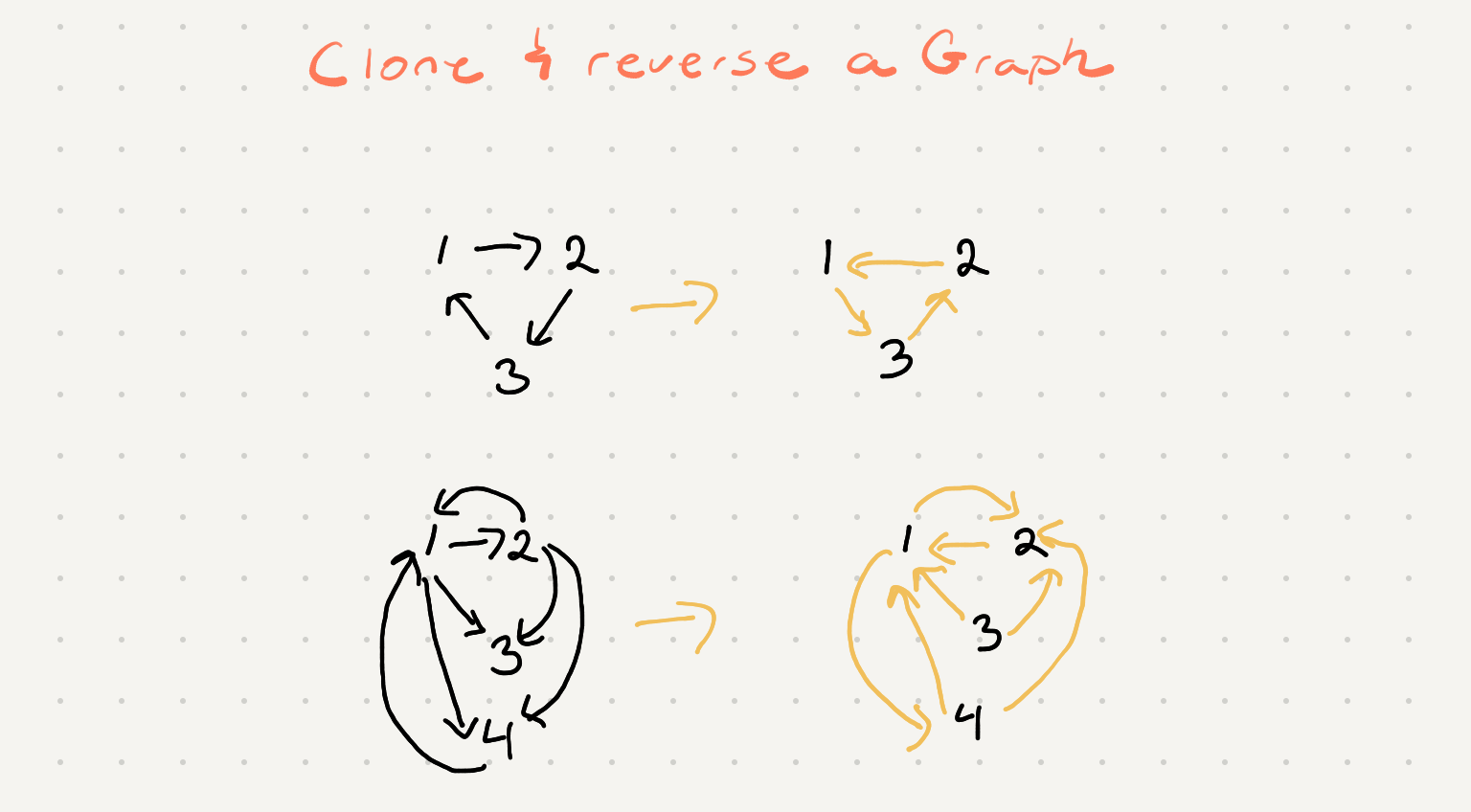
So we need to visit every node in our graph and create a clone and reverse the links. Visiting every node in our graph can be easily achieved via the standard bfs or dfs algorithm. Let’s remind ourselves what bfs looks like
from collections import Deque
def bfs(start):
visited = set()
q = deque()
q.append(start)
visited.append(start.val)
while q:
cur = q.popleft() # fifo
print(cur.data)
for n in cur.neighbors:
if (n.val not in visited):
q.append(n)
visted.append(n.val)
So what do we have to do to modify our bfs approach?
- Clone the actual explored graphs
- reverse the neighbor links
So #1 is easy to achieve as we can just create a new instance and copy over the values. #2 on the other hand is tricky because we have to have both the current value and the previous value to set the neighbor for the cloned copy. As we are traverse the graph we need a way to recall the previous value.
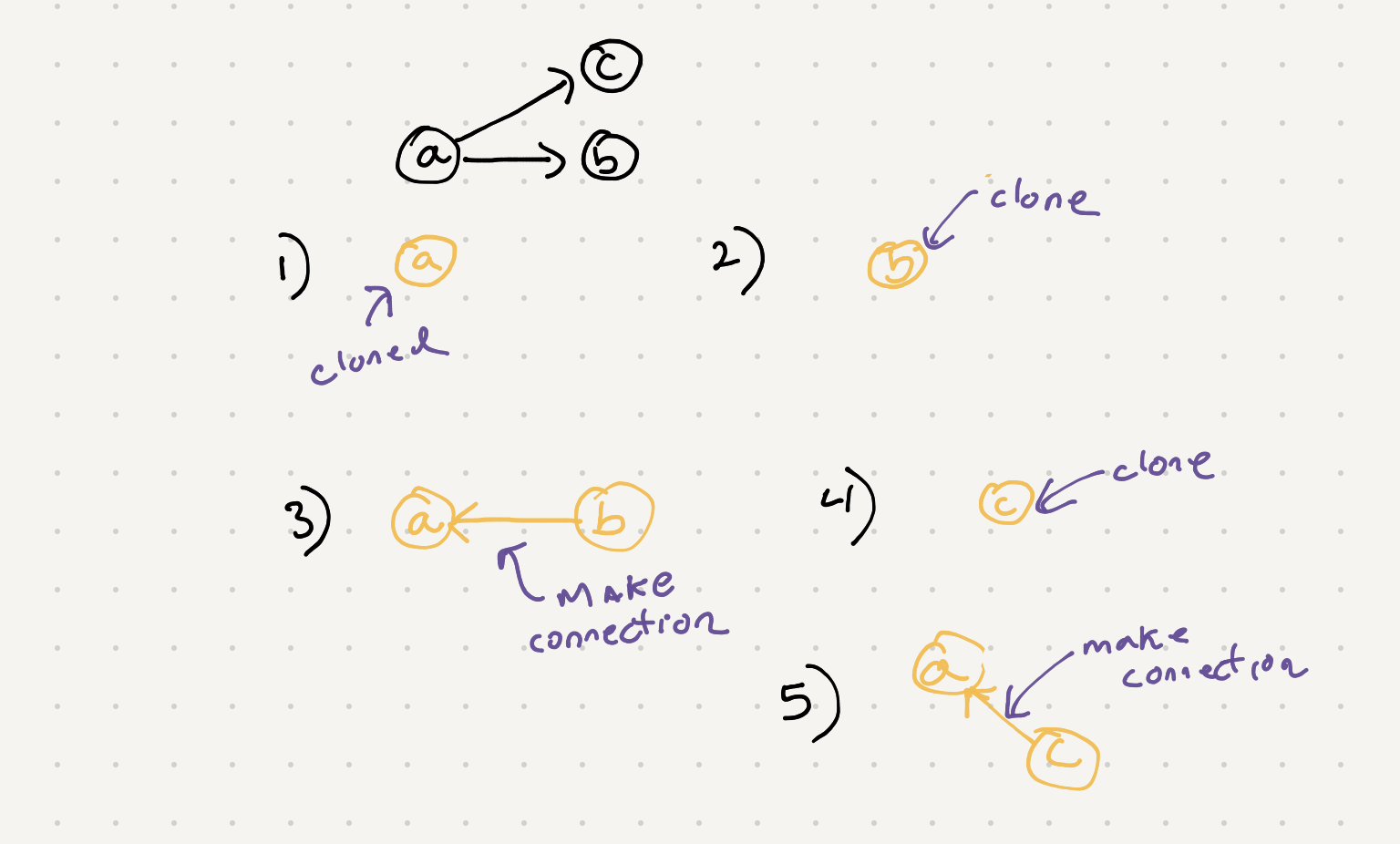
If we look at the steps we were have to make a connection it looks like we need to keep both the cloned versions of the connection. Now we can create nodes in each step of the while loop for our bfs but this is going to break when we have multiple connections in between nodes. We need to look up our existing cloned nodes when they have been created. One solution I came up with is to use a hashtable to store the cloned version of the current node.
By using this map we can get any existing nodes and keep appending them to the neighbors list. We also should prepopulate the hashtable with the inital cloned node so the first call to it doesn’t trigger an index error.
Putting it together we get
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.val = 0
self.neighbours = []
from collections import deque
def build_other_graph(node):
visited = set()
q = deque()
node_to_clone = Node()
node_to_clone.val = node.val
clone_dict = {}
clone_dict[node.val] = node_to_clone
q.append(node)
visited.add(node.val)
while q:
cur = q.popleft()
cloned_cur = clone_dict[cur.val]
if not cur.neighbours:
break
for neighbour in cur.neighbours:
if neighbour.val in clone_dict:
cloned_neighbour = clone_dict[neighbour.val]
else:
cloned_neighbour = Node()
cloned_neighbour.val = neighbour.val
cloned_neighbour.neighbours.append(cloned_cur)
clone_dict[neighbour.val] = cloned_neighbour
if neighbour.val not in visited:
visited.add(neighbour.val)
q.append(neighbour)
return node_to_clone
The runtime of this will be O(v+e)