Number of friend circles given a N x N matrix
Problem Statement:
There are N students in a class. Some of them are friends, while some are not. Their friendship is transitive in nature. For example, if A is a direct friend of B, and B is a direct friend of C, then A is an indirect friend of C. And we defined a friend circle is a group of students who are direct or indirect friends.
Given a N*N matrix M representing the friend relationship between students in the class. If M[i][j] = 1, then the ith and jth students are direct friends with each other, otherwise not. And you have to output the total number of friend circles among all the students.
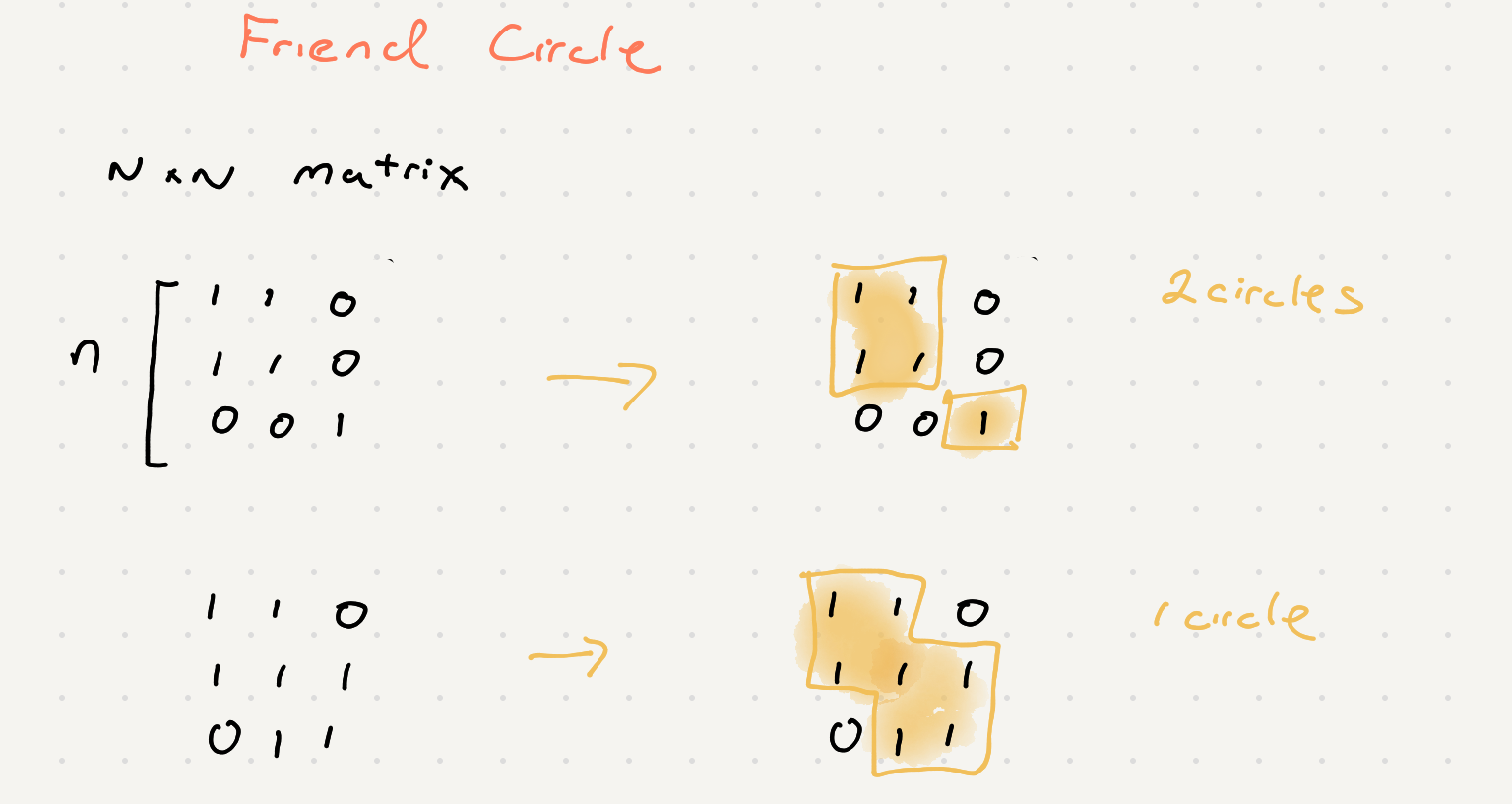
You will notice that the input matrix represents a truth table. A truth table shows the relation ship between different nodes. If we draw each person as a node in a graph we can use the table to draw a connection between the nodes
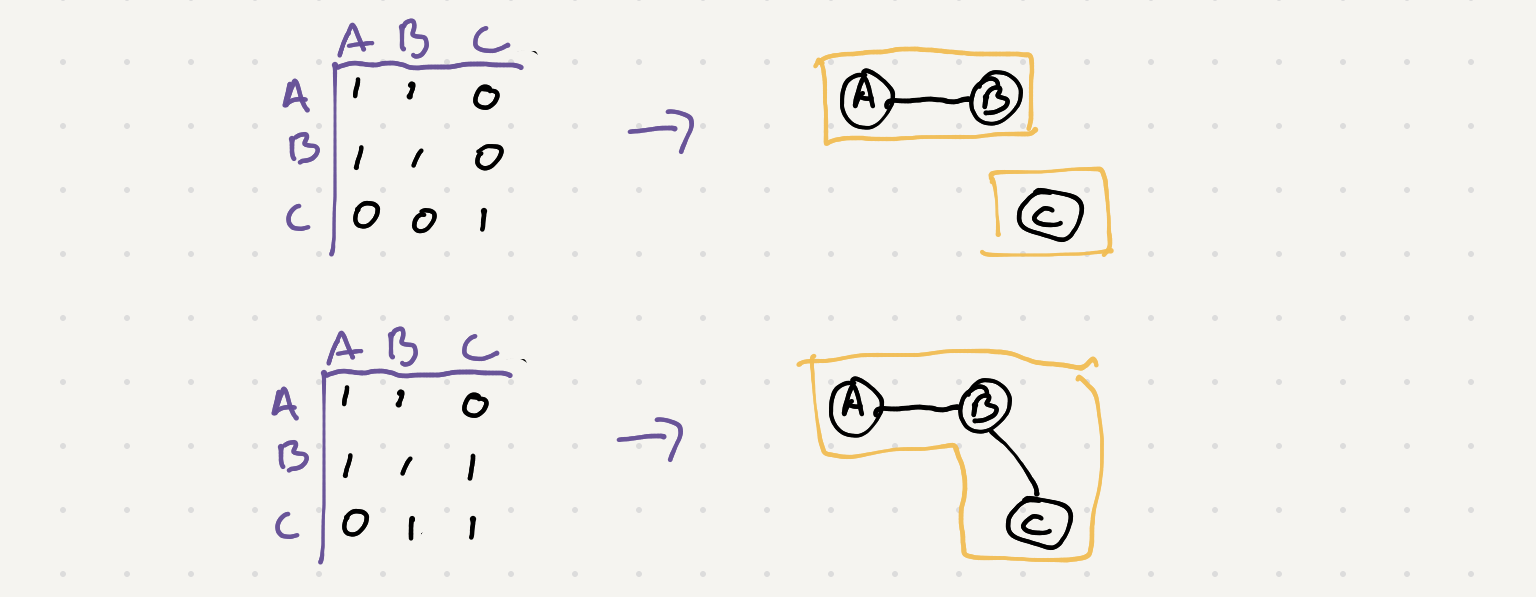
So we need to explore this graph and find all the isolated nodes. Let’s recall the standard DFS algorithm for exploring a graph
def dfs(list_of_vertices):
visited = set()
for v in list_of_vertices:
if v not in visited:
explore(v, visited)
def explore(node, visited):
visited.add(node)
for v in node.neighbors:
if (n not in seen):
explore(v, visited)
One special thing to note about this algorithm is the first for loop will account for unconnected items in the list of vertices. So if we had a graph with no nodes connected it would still explore each node.
So to solve this problem we need to do the following modifications to our base DFS code
-
Add a counter to track all the unconnected networks
-
We don’t have a way to get the neighbors so we’ll have to write a
get_neighborsfunction that can return all the nodes that are connected
To get a particular nodes neighbors we just have to example the row of values from our truth table.
So for example if we have a table
[
[1, 1, 0 , 0 1],
[1, 1, 0 , 0 0],
[0, 0, 1 , 1 0],
[0, 0, 1 , 1 0],
[1, 0, 0 , 0 1],
]
We want to look up the neighbors for the first friend which is at index 0
we would just iterate through the array at index 0 -> [1, 1, 0 , 0 1]
The first value in this case is the relationship to itself but since we are adding the element to the seen list it will be ignored and not visited again. We can just compare each value and add it to our neighbor list if the value is 1
Here’s an example of what the recursion tree would look like
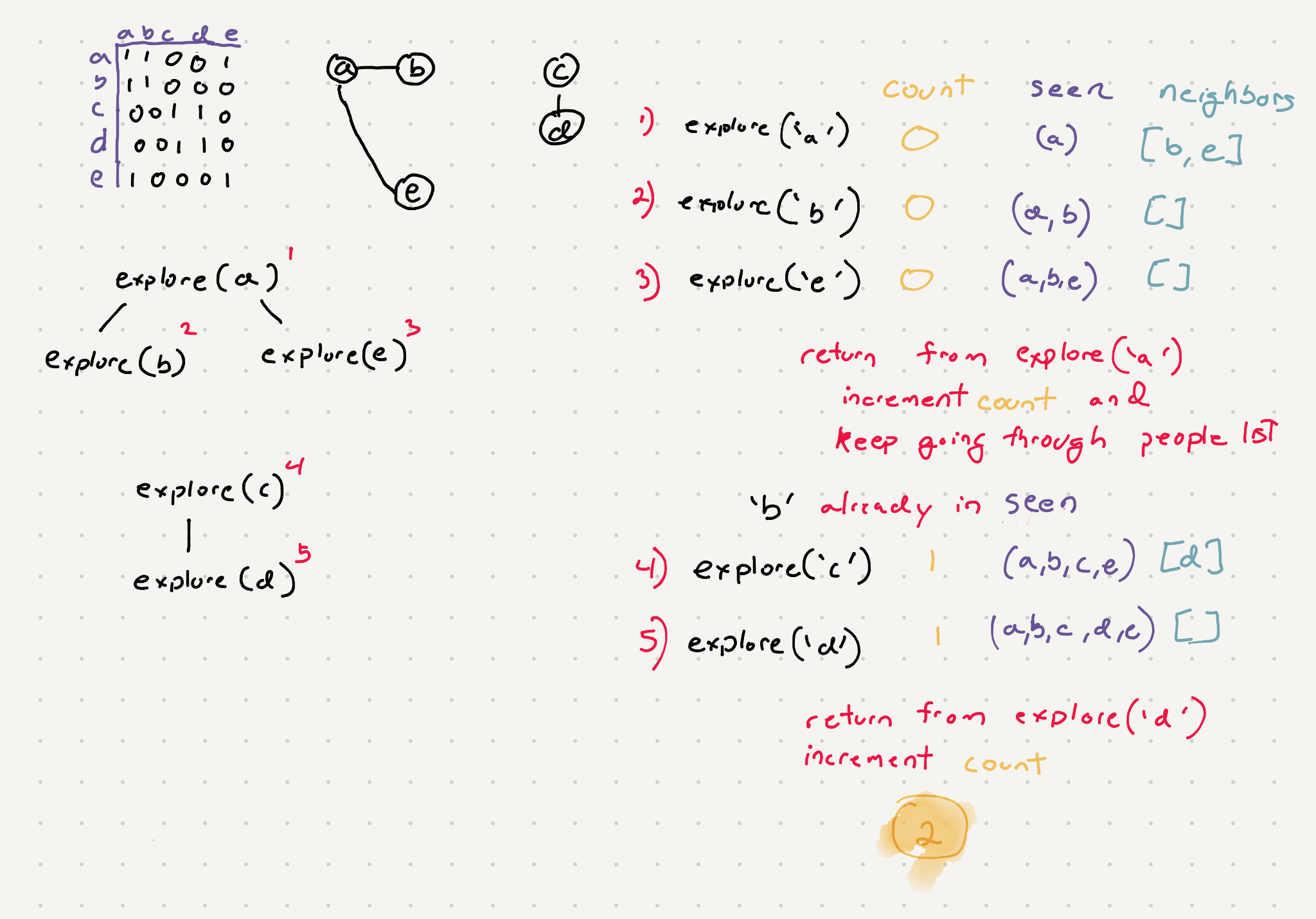
So adding our modifications we will have -
def findCircleNum(self, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def get_neighbors(vertex_index):
return (index for index, val in enumerate(M[vertex_index]) if val == 1)
def explore(vertex_index):
seen.add(vertex_index)
for new_vertex_index in get_neighbors(vertex_index):
if new_vertex_index not in seen:
explore(new_vertex_index)
seen = set()
cluster_count = 0
for vertex_index, vertex in enumerate(M):
if vertex_index not in seen:
cluster_count += 1
explore(vertex_index)
return cluster_count
Our runtime will be O(V+E)